SeekPCB is a leading manufacturer and supplier of rigid-flex PCBs, offering high-quality products and services to customers around the world. With years of experience in the PCB industry, SeekPCB has developed a reputation for excellence in the design, fabrication, and assembly of rigid-flex PCBs.
At SeekPCB, we understand the importance of quality and reliability in rigid-flex PCBs, which is why we use only the highest quality materials and the latest manufacturing techniques. Our state-of-the-art facilities are equipped with advanced equipment and technologies, allowing us to deliver products that meet or exceed the most demanding specifications.
We pride ourselves on our commitment to customer satisfaction, offering personalized service and support throughout every stage of the production process. From design and prototyping to full-scale production and delivery, we work closely with our customers to ensure that their rigid-flex PCBs meet their exact requirements. SeekPCB is capable of quick turn rigid-flex prototype with no MOQ regulation.
Whether you need a simple single-sided rigid-flex PCB or a complex multi-layer configuration, SeekPCB has the expertise and capabilities to deliver the highest quality products on time and on budget. Contact us today to learn more about our services and how we can help you with your rigid-flex PCB needs.
-
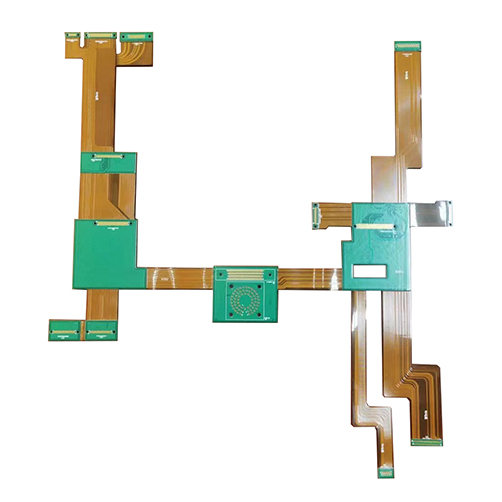 rigid flex
rigid flex -
 hdi rigid flex pcb
hdi rigid flex pcb -
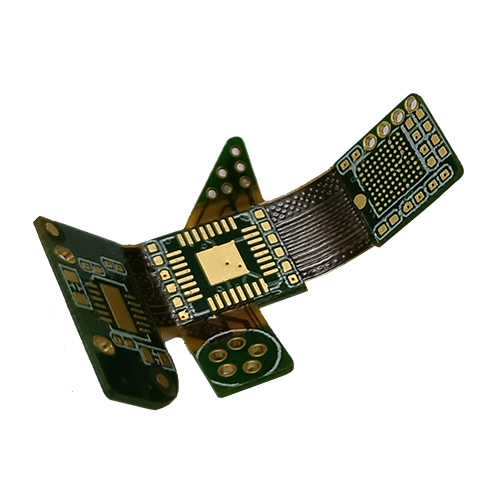 rigid flex circuit boards
rigid flex circuit boards -
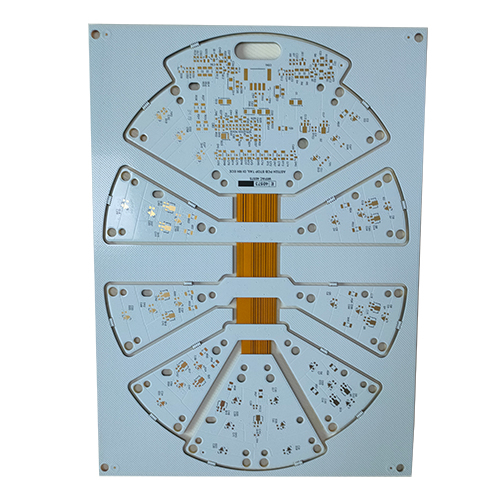 semi rigid flex pcb
semi rigid flex pcb -
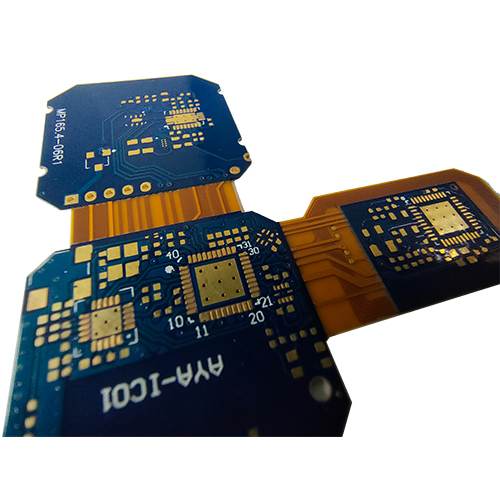 pcb rigid flex
pcb rigid flex -
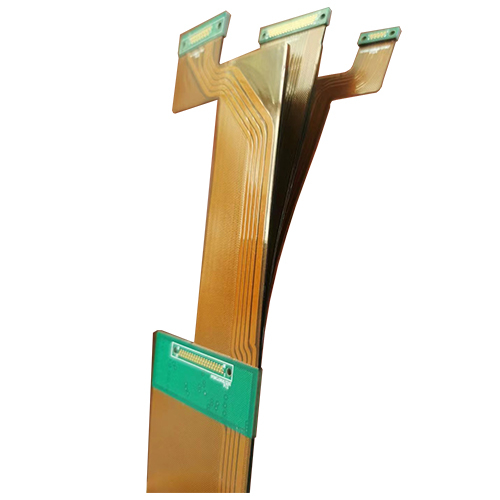 flexible rigid pcbWith 3 * 2L separable flexible boards, called flying tail structure
flexible rigid pcbWith 3 * 2L separable flexible boards, called flying tail structure
| Subject | Our Capability |
|---|---|
| Material Type | Rigid: FR4, Metal / Flex: PI / PP: No Flow |
| Rigid Flex Techniques | Air Gap, Fly Tail, Metal Base, HDI Rigid Flex |
| Layer | 2-24L with 16L Flexible Layers Max |
| FPC Impedance Control | Yes |
| Via In FPC | Yes |
| FPC Copper Thickness | 2OZ |
| Total Thickness | 0.4-6.5mm |
| Min. line width/spacing | 0.075mm/0.075mm |
| Min Hole Diameter | 0.1mm |
| Max. board Dimension | 400mm×550mm |
| Solder Mask | Green, Black, White, Red, Purple, Yellow, Orange, Blue, electromagnetic shielding film |
| Via Plug | Copper Fill, Resin Fill, POFV, VIPPO, Solder Mask Plug |
| Special Hole | Blind Hole, Blind Slot, T-Hole, T-Slot, Counter Sink Hole, Cup Hole, Counterbore |
| Surface treatment | OSP, ENIG, ENEPIG, Immersion Silver, Immersion Tin, Hard Gold |
| Outline | CNC Routing, V-CUT, Laser Routing |
- SEEKPCB Key Rigid Flex Technology 1
- Hole metallization in Flexible area
-
- SEEKPCB Key Rigid Flex Technology 2
- Coverlay fast pressing technology
-
- SEEKPCB Key Rigid Flex Technology 3
- Plasma surface & via technology
-
- SEEKPCB Key Rigid Flex Technology 4
- PP flow control technology
-
- SEEKPCB Key Rigid Flex Technology 5
- Flexible Layer Air Gap Technology
-
- SEEKPCB Key Rigid Flex Technology 6
- Metal Core Rigid Flex Hybration Lamination Technology
-
- SEEKPCB Key Rigid Flex Technology 7
- Laser Decap Technology
-
- SEEKPCB Key Rigid Flex Technology 8
- Multi-laser outline processing technology
-
- SEEKPCB Key Rigid Flex Technology 9
- Multi-layer electromagnetic shielding film lamination technology
-
- SEEKPCB Key Rigid Flex Technology 10
- Small-Spacing pre-decap technology
-
- SEEKPCB Key Rigid Flex Technology 11
- Laser cross-layer penetration Technology
-
Why Choose SEEKPCB as Your Rigid-Flex PCB Partner
2. All manufacturing is in the factory, delivery and quality controllable
3. Abundant material reserves, can meet the rapid sample delivery and small batch production
4. Quick turn service can be provided
5. All products will undergo strict reliability test and functional test before leaving the factory
6. Professional team, intervene from the beginning stage of design, accelerate PCB design speed, improve PCB manufacturability and cost competitiveness.
What is IC Rigid-Flex PCB
The main advantage of using a rigid-flex PCB is that it can eliminate the need for multiple interconnected PCBs, reducing assembly time and cost, as well as improving reliability by reducing the number of interconnects. Additionally, rigid-flex PCBs offer a higher level of design flexibility, as they can be shaped to fit into any space, and can be customized to meet the specific needs of a given application.
There are a number of different applications for rigid-flex PCBs, including in medical devices, aerospace, automotive, and consumer electronics. In general, any application that requires a high level of reliability, durability, and flexibility can benefit from the use of a rigid-flex PCB.
The advantages of rigid-flex PCB?
Rigid-flex PCBs offer several advantages over traditional rigid PCBs or flexible PCBs. Some of the key advantages of rigid-flex PCBs include:
Space-saving design: Rigid-flex PCBs can be designed to fit into tight or irregular spaces that would be difficult or impossible to accommodate with traditional rigid PCBs or flexible PCBs. This can allow for more compact and efficient designs.
Improved reliability: Rigid-flex PCBs can offer improved reliability compared to traditional rigid PCBs or flexible PCBs, since there are fewer interconnects and components. This can result in a lower risk of failures due to lose or broken connections.
Increased design flexibility: Rigid-flex PCBs offer a high level of design flexibility, as they can be shaped to fit into any space and can be customized to meet the specific needs of a given application. This can allow for more innovative and creative designs.
Cost savings: Rigid-flex PCBs can offer cost savings compared to traditional rigid PCBs or flexible PCBs, since they can eliminate the need for multiple interconnected PCBs, reducing assembly time and cost. Additionally, the improved reliability of rigid-flex PCBs can reduce maintenance and repair costs.
Improved signal integrity: Rigid-flex PCBs can offer improved signal integrity, as the shorter trace lengths and reduced interconnects can reduce signal noise and distortion.
Overall, the advantages of rigid-flex PCBs make them an attractive option for a wide range of applications, including in medical devices, aerospace, automotive, and consumer electronics.
what are the Rigid-flex PCB material?
Rigid-flex PCBs (Rigid-Flexible Printed Circuit Boards) are a combination of rigid and flexible PCBs that are joined together to create a single board with both rigid and flexible sections. The rigid sections provide mechanical support and protect the board from damage, while the flexible sections allow the board to bend, twist, or fold.
The materials used for rigid-flex PCBs are a combination of those used for rigid and flexible PCBs. For the rigid sections, the most commonly used materials are FR-4, a glass-reinforced epoxy laminate, and other high-performance materials, such as polyimide and Rogers 4000 series laminates, which offer better performance characteristics for certain applications. These materials are known for their high mechanical strength, excellent dimensional stability, and resistance to high temperatures. Also, SEEKPCB is capable of embedding metal plate into the rigid parts for better heat sink performance, as well as a stiffener to the flex part.
For the flexible sections, the most commonly used materials are polyimide (PI) and polyester (PET), which are the same materials used for flexible PCBs. These materials are chosen for their excellent flexibility and durability, which allows the board to bend, twist, or fold without breaking or damaging the conductive traces.
To join the rigid and flexible sections together, a specialized adhesive layer is used. The adhesive layer is typically made of a modified epoxy resin or acrylic adhesive that can bond the rigid and flexible sections together while still allowing them to move independently. This adhesive layer is also used to protect the conductive traces from damage due to mechanical stress or environmental factors, such as temperature and humidity.
Overall, the choice of materials for rigid-flex PCBs depends on the specific requirements of the application, such as temperature range, mechanical strength, and flexibility. A good understanding of the requirements of the application is important to select the right materials for the board to ensure that it performs effectively and reliably.
What are the typical structures of rigid-flex PCB.
There are several different structures or configurations that can be used for rigid-flex PCBs, depending on the specific application and design requirements. Here are some of the most common structures for rigid-flex PCBs:
Single-sided rigid-flex: In this structure, a single-sided rigid board is connected to a flexible circuit. This is the simplest and most cost-effective configuration, but it may not be suitable for all applications.
Double-sided rigid-flex: In this structure, two rigid boards are connected to a flexible circuit, with the flexible circuit sandwiched between the two rigid boards. This configuration can offer more design flexibility and better reliability than the single-sided structure.
Multi-layer rigid-flex: In this structure, multiple rigid boards are connected by flexible circuits, with multiple layers of flexible circuits sandwiched between the rigid boards. This configuration can offer even more design flexibility and reliability, but it is also more complex and expensive to manufacture.
Sculptured flex: In this structure, the flexible circuit is sculpted to fit the contours of the rigid board, creating a three-dimensional structure. This configuration can offer the most design flexibility and compactness, but it is also the most complex and expensive to manufacture.
Each of these structures has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of structure will depend on the specific requirements of the application.
For more detail rigid-flex stack up, pls refer to regid-flex structure.
The design rules of rigid-flex PCB?
Design rules for rigid-flex PCBs vary depending on the specific application, but there are some general guidelines that should be followed to ensure the reliability and manufacturability of the board. Here are some common design rules for rigid-flex PCBs:
Keep the bend radius in mind: Rigid-flex PCBs are designed to be bent and twisted, but it's important to keep the bend radius in mind. The bend radius is the minimum radius that the flexible part of the board can be bent without damaging the traces or the substrate. Typically, the bend radius should be at least 10 times the thickness of the thinnest layer in the board.
Avoid sharp corners: Sharp corners can cause stress concentration and can lead to cracking or breaking of the board. It's best to use rounded corners or fillets in the design to reduce stress concentration.
Keep the copper trace in mind: Copper traces are an important part of the design, and it's important to keep them in mind when designing the board. Copper traces on the flexible part of the board should be wider than on the rigid part of the board, as they will be subject to more stress during bending.
Use stiffeners: Stiffeners are used to reinforce the board in areas where it may be subject to stress or strain. Stiffeners are typically made of FR-4 or polyimide, and are bonded to the flexible part of the board to provide additional support.
Minimize the number of layers: The more layers in the board, the more difficult it is to manufacture and the more expensive it is. It's best to keep the number of layers to a minimum, and to use symmetrical stackups to ensure even distribution of stress.
Verify manufacturability: It's important to verify the manufacturability of the design before sending it to production. This includes checking for proper clearances, trace widths, and other design rules that are specific to the manufacturer's capabilities.
By following these design rules, you can create a reliable and manufacturable rigid-flex PCB that meets the requirements of your application. You can also check our rigid-flex PCB capability for more detail.
What are the difficulties in Rigid-Flex PCB manufacturing?
Manufacturing rigid-flex PCBs can be more challenging than traditional rigid PCBs or flexible PCBs, due to the complexity of the design and the manufacturing process. Some of the key difficulties in rigid-flex PCB manufacture include:
Materials selection: Rigid-flex PCBs require the use of specialized materials, such as flexible substrates and adhesives that can withstand the stresses of bending and flexing. Selecting the right materials can be a complex process that requires careful consideration of factors such as durability, flexibility, and electrical performance.
Design complexity: Rigid-flex PCBs are more complex to design than traditional rigid PCBs or flexible PCBs, as they require the integration of both rigid and flexible sections. This can make the design process more time-consuming and error-prone, as well as requiring specialized design software and tools.
Manufacturing process: Rigid-flex PCBs require specialized manufacturing processes that may be more time-consuming and expensive than those used for traditional rigid PCBs or flexible PCBs. For example, the manufacturing process may require multiple lamination steps and the use of specialized equipment for drilling, plating, and etching.
Quality control: Rigid-flex PCBs require a high degree of quality control to ensure that the final product meets the required specifications. This can be challenging, as defects can be difficult to detect and may not be apparent until after the PCB has been assembled.
Overall, the manufacture of rigid-flex PCBs requires specialized expertise and equipment, as well as a deep understanding of the design and manufacturing process. Despite these challenges, the benefits of rigid-flex PCBs make them an attractive option for a wide range of applications.
Optimizing the design of rigid-flex PCBs for better cost and reliability can be achieved through several methods. Here are some key strategies that can be used:
Simplify the design: One of the most effective ways to reduce the cost of rigid-flex PCBs is to simplify the design. This can be achieved by reducing the number of layers or the complexity of the circuitry, minimizing the use of special features like blind vias or buried vias, and avoiding complex shapes that require expensive tooling.
Optimize the materials: Selecting the right materials is critical for achieving optimal cost and reliability in rigid-flex PCBs. Using materials that are cost-effective and readily available, while still meeting the performance requirements of the design, can help to reduce costs. Additionally, selecting materials that are compatible with each other and can withstand the stresses of flexing and bending can help to improve the reliability of the PCB.
Minimize assembly complexity: The assembly process for rigid-flex PCBs can be complex and time-consuming, which can drive up costs. Minimizing the complexity of the assembly process can help to reduce costs and improve reliability. This can be achieved by reducing the number of assembly steps or using automated assembly methods.
Consider manufacturability early in the design process: Designing for manufacturability can help to optimize the design for better cost and reliability. This means taking into account the manufacturing process and capabilities of the PCB manufacturer early in the design process, and designing the PCB to be compatible with their equipment and processes.
Use simulation and testing: Simulating and testing the design of the rigid-flex PCB can help to identify potential issues early in the design process, before the PCB is manufactured. This can help to improve the reliability of the PCB, reduce the need for expensive rework, and ultimately reduce costs.
By implementing these strategies, it is possible to optimize the design of rigid-flex PCBs for better cost and reliability, while still meeting the performance requirements of the application.
How to optimize the cost and reliability of rigid-flex PCB
Manufacturing rigid-flex PCBs can be more challenging than traditional rigid PCBs or flexible PCBs, due to the complexity of the design and the manufacturing process. Some of the key difficulties in rigid-flex PCB manufacture include:
Materials selection: Rigid-flex PCBs require the use of specialized materials, such as flexible substrates and adhesives that can withstand the stresses of bending and flexing. Selecting the right materials can be a complex process that requires careful consideration of factors such as durability, flexibility, and electrical performance.
Design complexity: Rigid-flex PCBs are more complex to design than traditional rigid PCBs or flexible PCBs, as they require the integration of both rigid and flexible sections. This can make the design process more time-consuming and error-prone, as well as requiring specialized design software and tools.
Manufacturing process: Rigid-flex PCBs require specialized manufacturing processes that may be more time-consuming and expensive than those used for traditional rigid PCBs or flexible PCBs. For example, the manufacturing process may require multiple lamination steps and the use of specialized equipment for drilling, plating, and etching.
Quality control: Rigid-flex PCBs require a high degree of quality control to ensure that the final product meets the required specifications. This can be challenging, as defects can be difficult to detect and may not be apparent until after the PCB has been assembled.
Overall, the manufacture of rigid-flex PCBs requires specialized expertise and equipment, as well as a deep understanding of the design and manufacturing process. Despite these challenges, the benefits of rigid-flex PCBs make them an attractive option for a wide range of applications.
Optimizing the design of rigid-flex PCBs for better cost and reliability can be achieved through several methods. Here are some key strategies that can be used:
Simplify the design: One of the most effective ways to reduce the cost of rigid-flex PCBs is to simplify the design. This can be achieved by reducing the number of layers or the complexity of the circuitry, minimizing the use of special features like blind vias or buried vias, and avoiding complex shapes that require expensive tooling.
Optimize the materials: Selecting the right materials is critical for achieving optimal cost and reliability in rigid-flex PCBs. Using materials that are cost-effective and readily available, while still meeting the performance requirements of the design, can help to reduce costs. Additionally, selecting materials that are compatible with each other and can withstand the stresses of flexing and bending can help to improve the reliability of the PCB.
Minimize assembly complexity: The assembly process for rigid-flex PCBs can be complex and time-consuming, which can drive up costs. Minimizing the complexity of the assembly process can help to reduce costs and improve reliability. This can be achieved by reducing the number of assembly steps or using automated assembly methods.
Consider manufacturability early in the design process: Designing for manufacturability can help to optimize the design for better cost and reliability. This means taking into account the manufacturing process and capabilities of the PCB manufacturer early in the design process, and designing the PCB to be compatible with their equipment and processes.
Use simulation and testing: Simulating and testing the design of the rigid-flex PCB can help to identify potential issues early in the design process, before the PCB is manufactured. This can help to improve the reliability of the PCB, reduce the need for expensive rework, and ultimately reduce costs.
By implementing these strategies, it is possible to optimize the design of rigid-flex PCBs for better cost and reliability, while still meeting the performance requirements of the application.
+86-18925293263





















